DIVINE DEVOTION: EXPLORING THE HOLY ANOREXIA IN RELIGIOUS HISTORY
Delve into the intriguing world of holy anorexia, a phenomenon where religious devotees, particularly women, abstain from eating and drinking as an extreme act of devotion. This exploration examines the historical context, motivations, and controversies surrounding this practice, shedding light on the intersection of faith, self-denial, and spirituality.
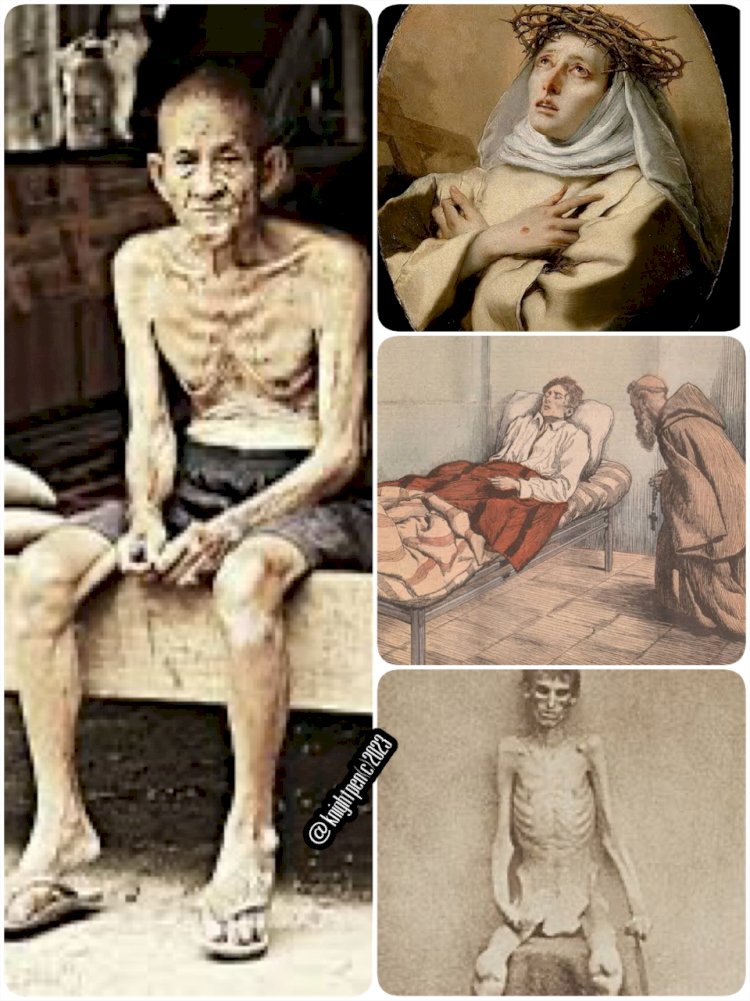
Holy anorexia, also known as anorexia mirabilis or inedia prodigiosa, refers to a phenomenon in religious history where individuals, typically women, are believed to abstain from eating and drinking for extended periods, often as a sign of religious devotion.
These individuals are revered within their communities for their extreme acts of self-denial, seen as a demonstration of spiritual strength and a deep connection with the divine.
Historically, holy anorexia has been associated with various religious traditions, including Christianity, Hinduism, and Buddhism. In Christian history, some notable figures believed to have experienced holy anorexia include Saint Catherine of Siena and Saint Clare of Assisi.
These women were said to have survived on minimal or no food for prolonged periods, subsisting only on the Eucharist or, in some cases, claiming to be nourished solely by the love of God.
The motivations behind holy anorexia are complex and multifaceted. For these individuals, refraining from food is often seen as a form of penance, a way to atone for the sins of humanity or to emulate the suffering of Christ. In some cases, it is also viewed as a means of transcending the physical body and achieving a higher state of spiritual purity.
However, it's essential to note that the phenomenon of holy anorexia has sparked debates and controversies within religious and medical communities. Skeptics argue that some cases might be attributed to psychological factors, such as self-induced starvation or mental health issues, rather than purely spiritual experiences.
From a medical perspective, prolonged fasting and extreme dietary restrictions can lead to severe health consequences, including malnutrition, electrolyte imbalances, and organ failure. Despite these risks, individuals experiencing holy anorexia are often deeply convinced of their spiritual calling and continue their practices despite the adverse effects on their health.
In contemporary society, the understanding and interpretation of holy anorexia continue to evolve. Some view it as a relic of the past, while others see it as a testament to the enduring power of faith and the human capacity for extraordinary religious experiences.
Regardless of one's perspective, the phenomenon of holy anorexia remains a fascinating and complex aspect of religious history, prompting discussions about the intersection of faith, devotion, and the human body.
You Can Also Read














